Prof. Yasuhiro Nakazawa1
Talk: "Drastic change of lattice heat capacity induced by electron correlations in molecular charge transfer complexes"
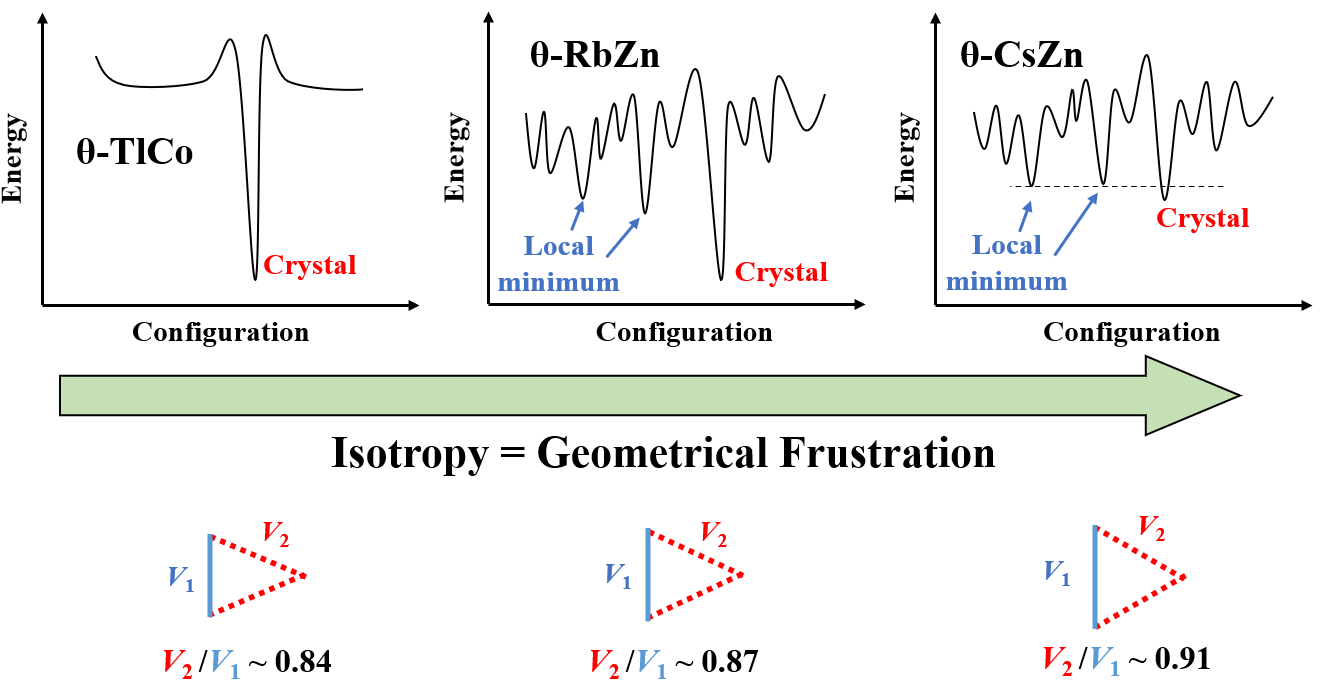
Wigner crystallization of electrons in two dimensional system with narrow band is interesting subject for condensed matter. Although it is a kind of theoretical subject, it appears in typical charge transfer complexes of organic donors and their counteranions. The 1/4 filling electronic state of π-electron band in M2X compounds where M denotes electron doner/acceptor molecules and X is monovalent counter ions inclined to show charge ordering (CO) state in which charge dendity in donor molecules has disproportionation, owing to the strong inter-site Coulomb repulsion V. Charge ordering (CO) and sepration with electron-rich and electron-poor molecules emerge spontaneously with superlattice periodicity and Wigner lattice type ordering is realized for example in (DI-DCNQI)2Ag, α-(BEDT-TTF)2I3 etc, where DCNQI is dicyanoquinonediimine and BEDT-TTF is bis(ethylenedithio)tetrathiafulvalene. However, if the molecular stacking in the electron donor/acceptor layer has frustration which disturbs formation of suitable charge ordering pattern, the glassy freezing of electron density manifest itself in low temperature region and make charge glass (CG) ground state. BEDT-TTF based charge-transfer salts with Θ-type donor arrangement is a typical material which shows such charge glass CG states as is shown in Fig. above [1-3].
We have developed a new apparatus to measure accurate heat capacity of a tiny single crystal sample less than 100μg of molecular compounds and have performed detail and systematic thermodynamic studies of these materials. Temperature dependences of the heat capacity of Θ-(BEDT-TTF)2CsZn(SCN)4, slowly cooled Θ-(BEDT-TTF)2RbZn(SCN)4, and Θ-(BEDT-TTF)2RbCo(SCN)4 are discussed in a wide temperature range below room tempearture down to 0.8 K. No thermal anomaly appears in the heat capacity in the first compound which means that this material do not show any long range ordering in the whole temperature range and show glassy freezing of charge distribution. We discuss possible dynamic feature occurs around the charge-glass (CG) formation tempearture based on the temperature and frequency dependence of the ac heat capacity measurement results. Freezing of charge destribution is dominated by actibation energy of about 2000 K in this case through the activation analysisof glassy dynamics. It is, however, emphasized that drastic change of lattice heat capacity was observed in the Θ-(BEDT-TTF)2RbZn(SCN)4 and also Θ-(BEDT-TTF)2RbCo(SCN)4 below the CO transition occurs. We discuss tempearture dependence of the heat capacity of Θ-(BEDT-TTF)2RbZn(SCN)4 and investigate large difference of phonon state between well-ordered CO state and glassy state. A hystertic behavior in the lattice heat capacity occurs in this compound through the CO transitions originates from very strong coupling between charge and lattice degrees of freedom.
- [1] R. Yoshimoto et al. Physica B 2014, 449, 19-24
- [2] T. Nomoto and Y. Nakazawa et al. J. Phys. Soc. Jpn. 2019, 88, 073601 1-4
- [3] T. Nomoto and Y. Nakazawa et al. Phys. Rev. B 2023, 107, 124803 1-7.
Acknowledgements: This work was partially supported by JSPS KAKENHI Grant Numbers: JP20H01862 and JP24K00571.